How Do I Pass Back Return Values From the Function Matlab
C function argument and return values
Prerequisite : Functions in C/C++
A function in C can be called either with arguments or without arguments. These function may or may not return values to the calling functions. All C functions can be called either with arguments or without arguments in a C program. Also, they may or may not return any values. Hence the function prototype of a function in C is as below:
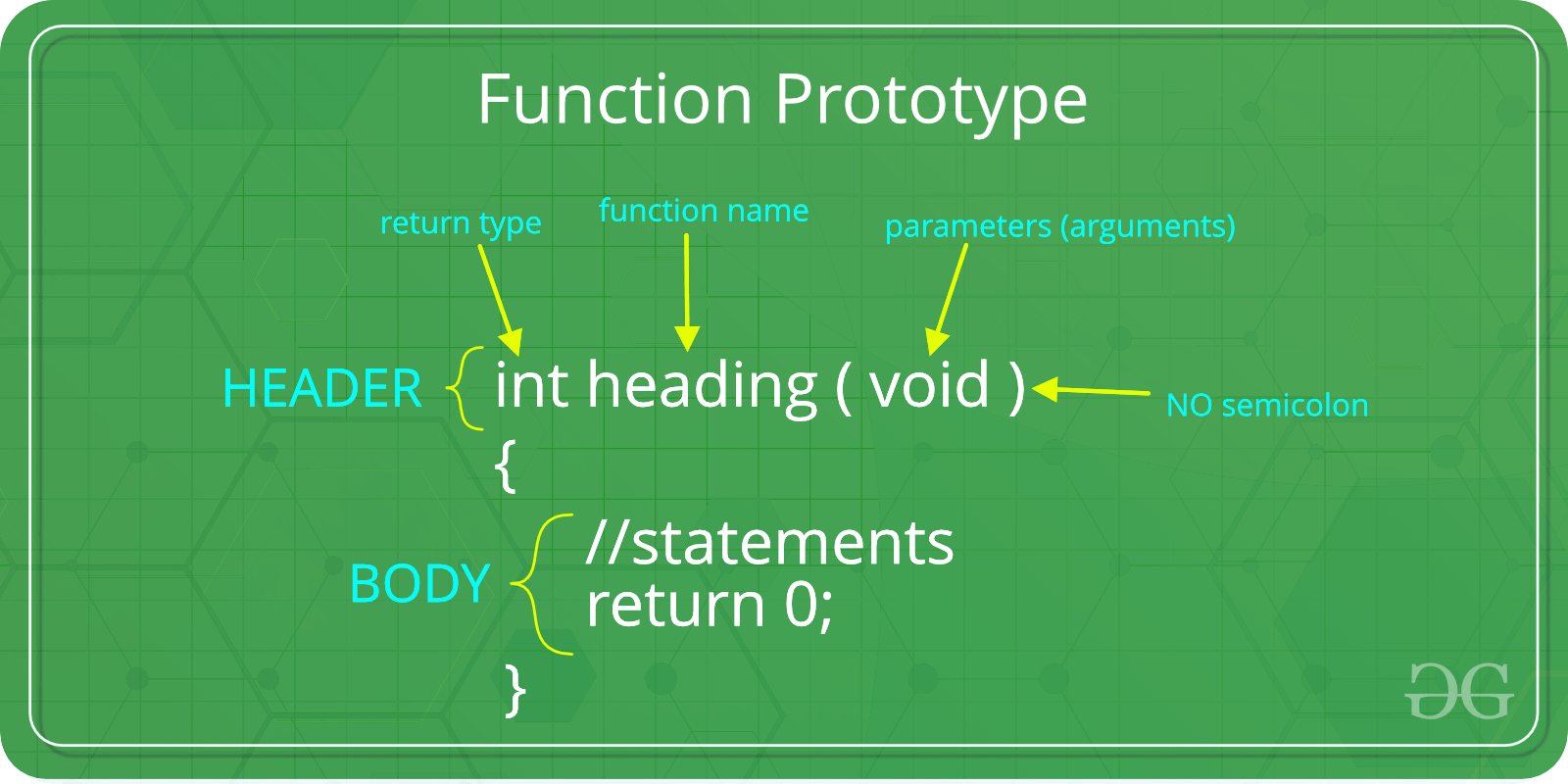
Want to learn from the best curated videos and practice problems, check out the C++ Foundation Course for Basic to Advanced C++ and C++ STL Course for foundation plus STL. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course .
There are following categories:
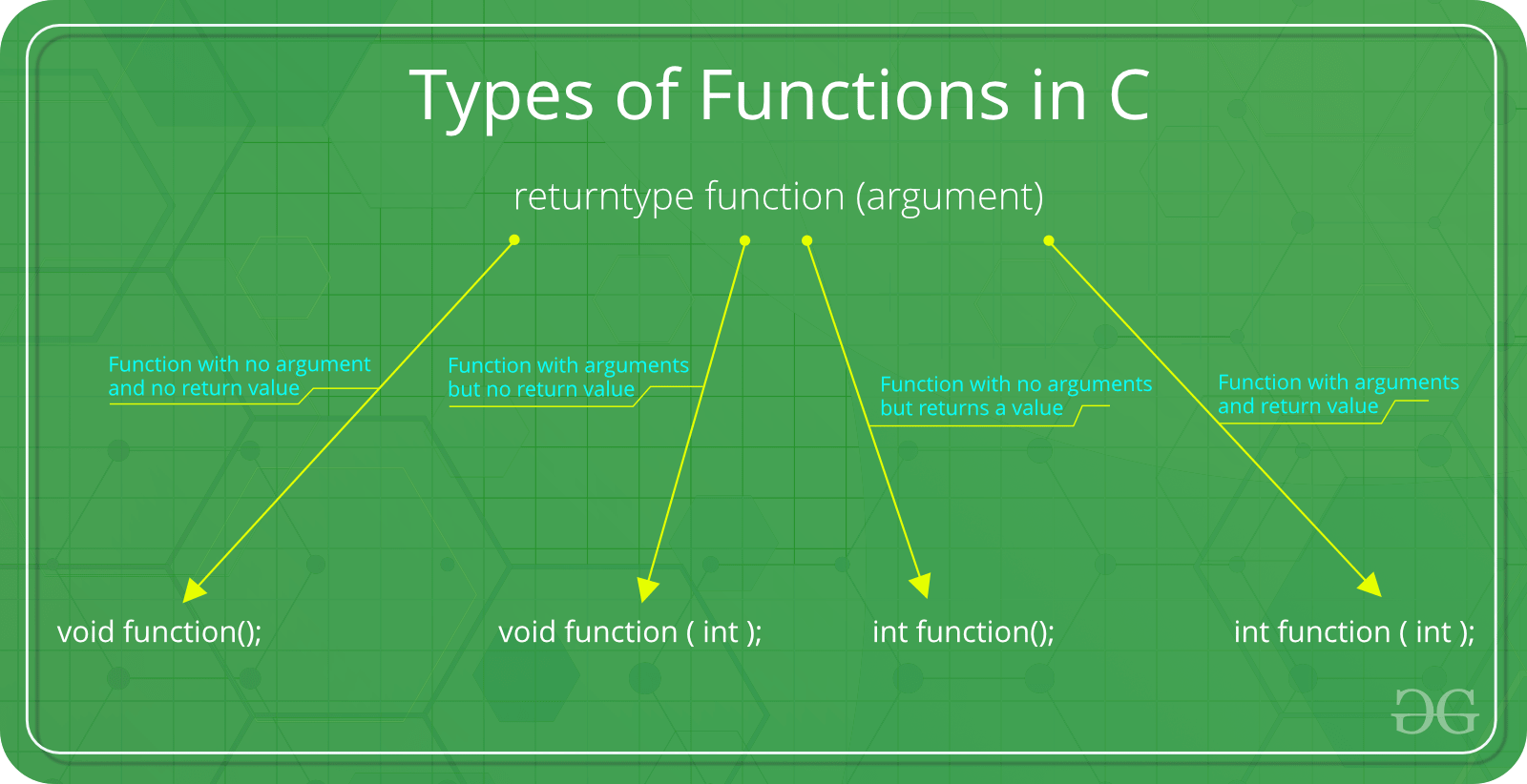
- Function with no argument and no return value : When a function has no arguments, it does not receive any data from the calling function. Similarly when it does not return a value, the calling function does not receive any data from the called function.
Syntax :Function declaration : void function(); Function call : function(); Function definition : void function() { statements; }#include <stdio.h>voidvalue(void);voidmain(){value();}voidvalue(void){intyear = 1, period = 5, amount = 5000, inrate = 0.12;floatsum;sum = amount;while(year <= period) {sum = sum * (1 + inrate);year = year + 1;}printf(" The total amount is %f:", sum);}Output:
The total amount is 5000.000000
- Function with arguments but no return value : When a function has arguments, it receive any data from the calling function but it returns no values.
Syntax :
Function declaration : void function ( int ); Function call : function( x ); Function definition: void function( int x ) { statements; }#include <stdio.h>voidfunction(int,int[],char[]);intmain(){inta = 20;intar[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };charstr[30] ="geeksforgeeks";function(a, &ar[0], &str[0]);return0;}voidfunction(inta,int* ar,char* str){inti;printf("value of a is %d\n\n", a);for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("value of ar[%d] is %d\n", i, ar[i]);}printf("\nvalue of str is %s\n", str);}Output:
value of a is 20 value of ar[0] is 10 value of ar[1] is 20 value of ar[2] is 30 value of ar[3] is 40 value of ar[4] is 50 The given string is : geeksforgeeks
- Function with no arguments but returns a value : There could be occasions where we may need to design functions that may not take any arguments but returns a value to the calling function. A example for this is getchar function it has no parameters but it returns an integer an integer type data that represents a character.
Syntax :Function declaration : int function(); Function call : function(); Function definition : int function() { statements; return x; }#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>intsum();intmain(){intnum;num = sum();printf("\nSum of two given values = %d", num);return0;}intsum(){inta = 50, b = 80, sum;sum =sqrt(a) +sqrt(b);returnsum;}Output:
Sum of two given values = 16
- Function with arguments and return value
Syntax :Function declaration : int function ( int ); Function call : function( x ); Function definition: int function( int x ) { statements; return x; }#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>intfunction(int,int[]);intmain(){inti, a = 20;intarr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };a = function(a, &arr[0]);printf("value of a is %d\n", a);for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("value of arr[%d] is %d\n", i, arr[i]);}return0;}intfunction(inta,int* arr){inti;a = a + 20;arr[0] = arr[0] + 50;arr[1] = arr[1] + 50;arr[2] = arr[2] + 50;arr[3] = arr[3] + 50;arr[4] = arr[4] + 50;returna;}Output:
value of a is 40 value of arr[0] is 60 value of arr[1] is 70 value of arr[2] is 80 value of arr[3] is 90 value of arr[4] is 100
How Do I Pass Back Return Values From the Function Matlab
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-function-argument-return-values/
0 Response to "How Do I Pass Back Return Values From the Function Matlab"
Post a Comment